Cochlear Implant
Need help?
Need help with your hearing? We offer comprehensive hearing services to improve your quality of life.
+8801858 200 300
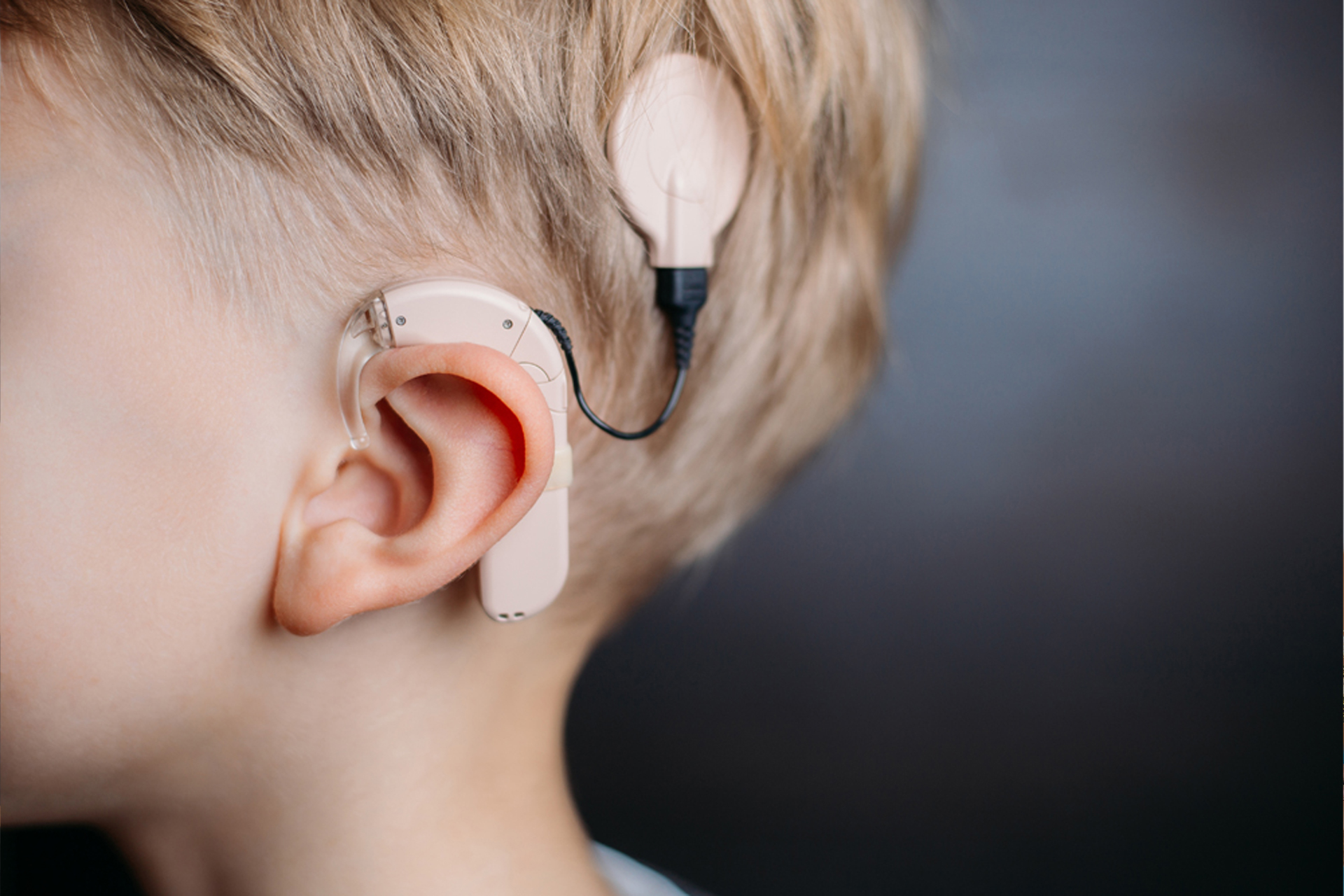
Cochlear Implant
A cochlear implant is a revolutionary medical device designed to restore hearing to individuals with severe to profound hearing loss who gain limited benefit from hearing aids. Unlike hearing aids, which amplify sound, cochlear implants bypass damaged parts of the inner ear (cochlea) to directly stimulate the auditory nerve. The device consists of an external component worn behind the ear and an internal component surgically implanted under the skin.
Hearing renewed, life transformed: Cochlear Implants bring sound to the silent world.
The external part captures sound and processes it into digital signals, which are then transmitted to the internal part and converted into electrical impulses. These impulses are sent to the auditory nerve, which carries them to the brain, where they are perceived as sound. With proper rehabilitation and therapy, cochlear implant recipients can improve their speech understanding and communication skills, enhancing their quality of life and enabling them to engage more fully in social interactions and daily activities.

Our benefits
Cochlear implants offer improved speech understanding, enhanced communication, and increased social engagement for those with severe hearing loss. They restore auditory function, enriching quality of life and facilitating daily interactions.
What is a cochlear implant?
A cochlear implant is a medical device that bypasses damaged parts of the inner ear to stimulate the auditory nerve directly. It consists of an external processor and an internal electrode array, working together to convert sound into electrical signals that the brain perceives as sound, aiding severe hearing loss.
Who is a candidate for a cochlear implant?
A candidate for a cochlear implant typically has severe to profound hearing loss in both ears and receives limited benefit from hearing aids. They often struggle to understand speech even with amplification. Evaluation by an audiologist and an ear, nose, and throat specialist determines candidacy based on specific criteria.
How does a cochlear implant work?
A cochlear implant works by bypassing damaged parts of the inner ear to directly stimulate the auditory nerve. It consists of an external processor that captures sound, processes it into digital signals, and transmits them to an internal receiver. The receiver sends these signals to the auditory nerve, allowing sound perception.
What are the benefits of cochlear implants?
Cochlear implants offer improved speech understanding and communication for those with severe to profound hearing loss. They enhance social engagement, facilitate daily interactions, and can significantly improve the quality of life by restoring auditory function and enabling recipients to connect more fully with the world around them.
